Abstract of Publication No. 487
 Pascal Gerner, Christine Reinhard and Hans U. Güdel
Pascal Gerner, Christine Reinhard and Hans U. Güdel
Cooperative Near-IR to Visible Photon Upconversion in Yb3+-Doped MnCl2 and MnBr2:
Comparison with a Series of Yb3+-Doped Mn2+ Halides
Chem. Eur. J. 10, 4735-4741 (2004)
![]()
![]()
Abstract:
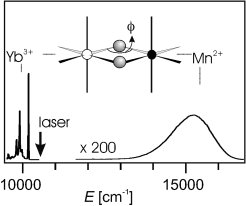
Yb3+-doped MnCl2 and MnBr2 crystals exhibit
strong red upconversion luminescence under near-infrared excitation around
10 000 cm–1 at temperatures below 100 K. The broad red luminescence
band is centred around 15 200 cm–1 for both compounds and identified
as the Mn2+ 4T1g![]() 6A1g
transition. Excitation with 10 ns pulses
indicates that the upconversion process consists of a sequence of ground-state
and excited-state absorption steps. The experimental VIS/NIR photon ratio at 12
K for an excitation power of 191 mW focused on the sample with a 53 mm lens is
4.1 % for MnCl2:Yb3+ and 1.2 % for
MnBr2:Yb3+. An upconversion mechanism based on exchange
coupled Yb3+-Mn2+ ions is proposed. Similar upconversion
properties have been reported for RbMnCl3:Yb3+,
CsMnCl3:Yb3+, CsMnBr3:Yb3+,
RbMnBr3:Yb3+,
Rb2MnCl4:Yb3+. The efficiency of the
upconversion process in these compounds is strongly dependent on the
connectivity between the Yb3+ and Mn2+ ions. The VIS/NIR
photon ratio decreases by three orders of magnitude along the series of
corner-sharing Yb3+-Cl–-Mn2+, edge-sharing
Yb3+-(Cl–)2-Mn2+ to face-sharing
Yb3+-(Br–)3-Mn2+ bridging geometry.
This trend is discussed in terms of the dependence of the relevant
super-exchange pathways on the Yb3+-Mn2+ bridging
geometry.
6A1g
transition. Excitation with 10 ns pulses
indicates that the upconversion process consists of a sequence of ground-state
and excited-state absorption steps. The experimental VIS/NIR photon ratio at 12
K for an excitation power of 191 mW focused on the sample with a 53 mm lens is
4.1 % for MnCl2:Yb3+ and 1.2 % for
MnBr2:Yb3+. An upconversion mechanism based on exchange
coupled Yb3+-Mn2+ ions is proposed. Similar upconversion
properties have been reported for RbMnCl3:Yb3+,
CsMnCl3:Yb3+, CsMnBr3:Yb3+,
RbMnBr3:Yb3+,
Rb2MnCl4:Yb3+. The efficiency of the
upconversion process in these compounds is strongly dependent on the
connectivity between the Yb3+ and Mn2+ ions. The VIS/NIR
photon ratio decreases by three orders of magnitude along the series of
corner-sharing Yb3+-Cl–-Mn2+, edge-sharing
Yb3+-(Cl–)2-Mn2+ to face-sharing
Yb3+-(Br–)3-Mn2+ bridging geometry.
This trend is discussed in terms of the dependence of the relevant
super-exchange pathways on the Yb3+-Mn2+ bridging
geometry.