Abstract of Publication No. 492
 A. Bessière, P. Dorenbos, C. W. E. van Eijk, K. Krämer and H. U. Güdel
A. Bessière, P. Dorenbos, C. W. E. van Eijk, K. Krämer and H. U. Güdel
New thermal neutron scintillators: Cs2LiYCl6 : Ce3+
and Cs2LiYBr6 : Ce3+
IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 51, 2970-2972 (2004)
![]()
![]()
Abstract:
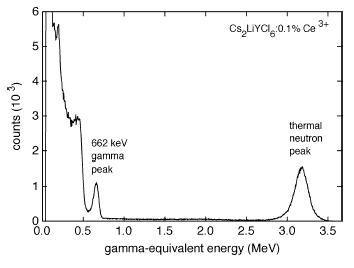
The thermal neutron detection properties of Cs2LiYCl6:0.1%Ce3+
and Cs2LiYBr6:1%Ce3+ single
crystals are presented. The compounds show high scintillation photon yields of
70 000 and 88 200 photons emitted per absorbed thermal neutron, respectively.
Events caused by primary electrons with energy below 2.9 and 3.4 MeV,
respectively, can be separated from neutron-induced events by pulse-height
discrimination. For Cs2LiYCl6:0.1Ce3+, due to the presence of
a 4-ns fast core-valence luminescence, thermal neutrons and gamma rays can also
be discriminated by means of the shape of the scintillation pulse. The main part
of the scintillation pulse in Cs2LiYCl6:0.1%Ce3+ is relatively
slow, however, Cs2LiYBr6:1%Ce3+ has a relatively intense
component with t = 85 ns decay time.