Abstract of Publication No. 518
 J. F. Suyver, J. Grimm, K. W. Krämer and H. U. Güdel
J. F. Suyver, J. Grimm, K. W. Krämer and H. U. Güdel
Highly efficient near-infrared to visible up-conversion process in
NaYF4:Er3+,Yb3+
J. Lumin. 114, 53-59 (2005)
![]()
![]()
Abstract:
Up-conversion (UC) entails the addition of two (or more) photons to generate one
of higher energy. This process is very interesting, both from a fundamental
point of view as well as for (future) applications. Here, dependence of the
emission spectra on excitation power and measurement temperature are reported
for the very efficient near-infrared to visible photon UC material NaYF4:
2% Er3+, 18% Yb3+.
In the high-power limit for continuous-wave laser excitation, roughly 50% of all
near-infrared photons absorbed by the material are up-converted and emitted in
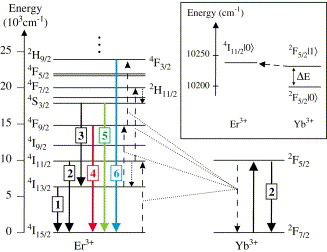
the visible spectral range. The excitation spectrum shows a 39 cm–1
energy gap between the two lowest crystal-field components |0> and |1> of
the Yb3+ 2F5/2 multiplet, which sensitizes the UC
emission. There is very efficient energy transfer to the lowest energy
crystal-field component of the Er3+ 4I11/2
state from 2F5/2|1>, resulting in an activation energy for
all Er3+
related up- and down-conversion emissions that scales with the number of
excitation photons required multiplied by the 39 cm–1 energy gap.