Abstract of Publication No. 526
 Sara García-Revilla, Pascal Gerner, Hans U. Güdel and Rafael Valiente
Sara García-Revilla, Pascal Gerner, Hans U. Güdel and Rafael Valiente
Yb3+-sensitized visible Ni2+ photon upconversion in codoped
CsCdBr3 and CsMgBr3
Phys. Rev. B 72, 125111/1-9 (2005)
![]()
![]()
Abstract:
Near-infrared excitation of
Yb3+ 2F7/2 ![]() 2F5/2 at 10600 cm–1 in the
linear chain CsMBr3:Ni2+,Yb3+ (M=Cd,Mg)
structure leads to green luminescence from Yb3+ pairs and
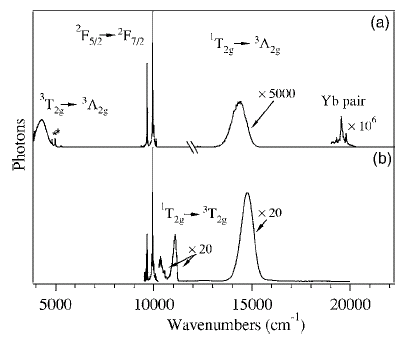
red Ni2+ upconversion luminescence at cryogenic
temperatures. The broad red upconversion luminescence is assigned to
the 1T2g
2F5/2 at 10600 cm–1 in the
linear chain CsMBr3:Ni2+,Yb3+ (M=Cd,Mg)
structure leads to green luminescence from Yb3+ pairs and
red Ni2+ upconversion luminescence at cryogenic
temperatures. The broad red upconversion luminescence is assigned to
the 1T2g ![]() 3A2g transition of Ni2+.
The upconversion excitation spectrum indicates that the active
mechanism in these systems involves both Yb3+ and
Ni2+ ions. Lifetime and power dependence data allow one to
identify a ground-state-absorption (GSA) energy-transfer upconversion
(ETU) as the underlying upconversion mechanism for the
Yb3+-Ni2+ system in doubly doped
CsCdBr3 and CsMgBr3. A less efficient
single-ion GSA excited-state-absorption (ESA) process within
Ni2+ is also observed in the title compounds. However,
whereas the GSA/ESA process requires an excitation energy above
11200 cm–1, it is possible to sensitize the
Ni2+ upconversion via Yb3+ excitation at energies around
10200 cm–1 and around 10600 cm–1 in
CsCdBr3 and CsMgBr3. It is shown that only
those Ni2+ ions neighboring to Yb3+ ions are
relevant for the upconversion induced by Yb3+ excitation.
3A2g transition of Ni2+.
The upconversion excitation spectrum indicates that the active
mechanism in these systems involves both Yb3+ and
Ni2+ ions. Lifetime and power dependence data allow one to
identify a ground-state-absorption (GSA) energy-transfer upconversion
(ETU) as the underlying upconversion mechanism for the
Yb3+-Ni2+ system in doubly doped
CsCdBr3 and CsMgBr3. A less efficient
single-ion GSA excited-state-absorption (ESA) process within
Ni2+ is also observed in the title compounds. However,
whereas the GSA/ESA process requires an excitation energy above
11200 cm–1, it is possible to sensitize the
Ni2+ upconversion via Yb3+ excitation at energies around
10200 cm–1 and around 10600 cm–1 in
CsCdBr3 and CsMgBr3. It is shown that only
those Ni2+ ions neighboring to Yb3+ ions are
relevant for the upconversion induced by Yb3+ excitation.