Abstract of Publication No. 556
 K. M. Mogare, D. V. Sheptyakov, R. Bircher, H.-U. Güdel and M. Jansen
K. M. Mogare, D. V. Sheptyakov, R. Bircher, H.-U. Güdel and M. Jansen
Neutron diffraction study of the magnetic structure of Na2RuO4
Eur. Phys. J. B 52, 371-376 (2006)
![]()
![]()
Abstract:
Nuclear and magnetic structures of sodium ruthenate (VI) have been studied by
neutron powder diffraction in the temperature range 1.5–200 K.
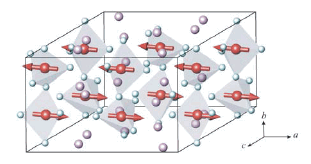
Na2RuO4 crystallizes in the monoclinic structure, with
space group P 21/c. The structure consists of apical corner sharing
RuO5 trigonal bipyramids forming infinite chains running along the b
axis. These infinite [ RuO3O2/2] chains form a pseudo
hexagonal close packing of rods with Ru–Ru distances of 3.51 Å within the chains
and 5.30–5.47 Å between the chains. At TN = 37.2 K a magnetic
transition leads to an antiferromagnetic state. The Ru6+ magnetic
moments are ordered antiferromagnetically along the chains (b-axis), while the
inter-chain interaction is ferromagnetic. A classical infinite chain model was
fitted to the magnetic susceptibility data in order to estimate the strength of
the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions along and between the chains,
resulting in an intrachain coupling parameter of 2J = -86 K, and an interchain
parameter J![]() with |2J
with |2J![]() | = 3 K.
| = 3 K.