Abstract of Publication No. 560
 Eva Beurer, Judith Grimm, Pascal Gerner and Hans U. Güdel
Eva Beurer, Judith Grimm, Pascal Gerner and Hans U. Güdel
Absorption, Light Emission, and Upconversion Properties of
Tm2+-Doped CsCaI3 and RbCaI3
Inorg. Chem. 45, 9901-9906 (2006)
![]()
![]()
Abstract:
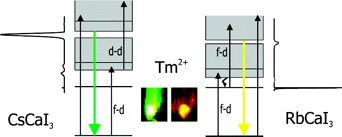
Absorption, light emission, and upconversion properties of Tm2+-doped
CsCaI3 and RbCaI3 single crystals are presented and
compared. Both compounds show multiple emissions after excitation at 21834
cm–1 between 10 and 300 K. Besides sharp 4f-4f transitions
around 8800 cm–1, five and three broad 4f-5d emission
bands are observed at higher energies in CsCaI3:Tm2+ and
RbCaI3:Tm2+, respectively. The 4f-5d transitions are very
sensitive to the crystalline environment: the onset of the 4f-5d excitations is
red-shifted by about 1000 cm–1 in
RbCaI3:Tm2+ compared to CsCaI3:Tm2+.
In addition, a broadening of bands is observed in the former compound. These
differences are attributed to the structural changes that occur when the alkali
metal is changed from Cs to Rb in these crystal lattices. An increased energy
splitting of the multiplets and a red shift of the barycenter of the
(4f)12(5d)1 electron configuration in
RbCaI3:Tm2+ is the result. This affects not only the color
of the visible emission, which turns from green in
CsCaI3:Tm2+ to yellow in
RbCaI3:Tm2+, but also the excited state dynamics. As a
consequence, the dominant upconversion processes are different in the two
compounds. Thus, the two title compounds nicely illustrate the influence of the
structural environment on the optical spectroscopic properties of
Tm2+.